
- #WIFI SIGNAL STRENGTH APP FOR MAC FOR ANDROID#
- #WIFI SIGNAL STRENGTH APP FOR MAC MAC#
- #WIFI SIGNAL STRENGTH APP FOR MAC WINDOWS#
Quick guide: OS X Mavericks for Windows switchers.OS X Mavericks: Fixing wireless keyboard/mouse connections.OS X Mavericks, iOS 7: Text Shortcuts explained.Troubleshooting tips for Apple Mail on OS X Mavericks.
#WIFI SIGNAL STRENGTH APP FOR MAC FOR ANDROID#
#WIFI SIGNAL STRENGTH APP FOR MAC MAC#
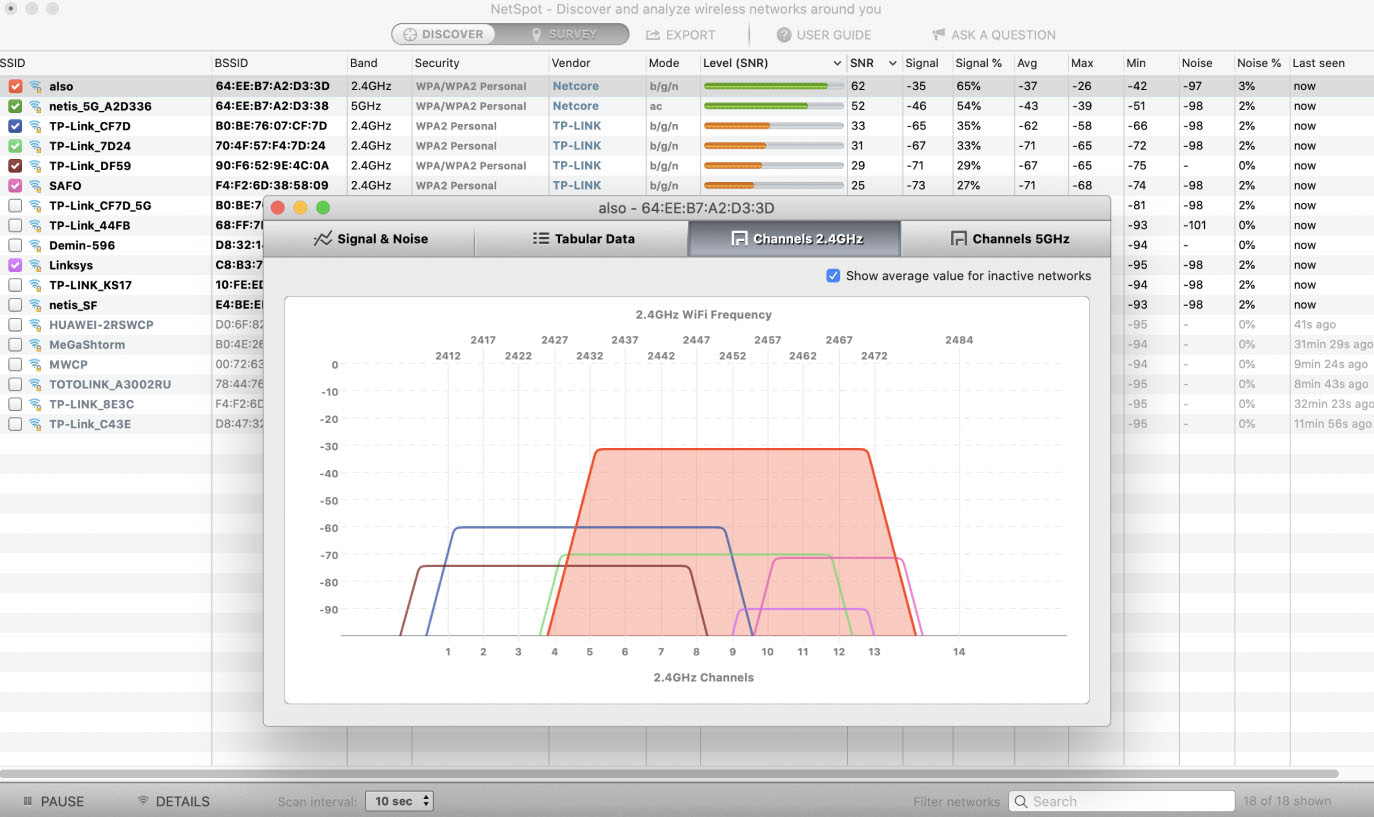
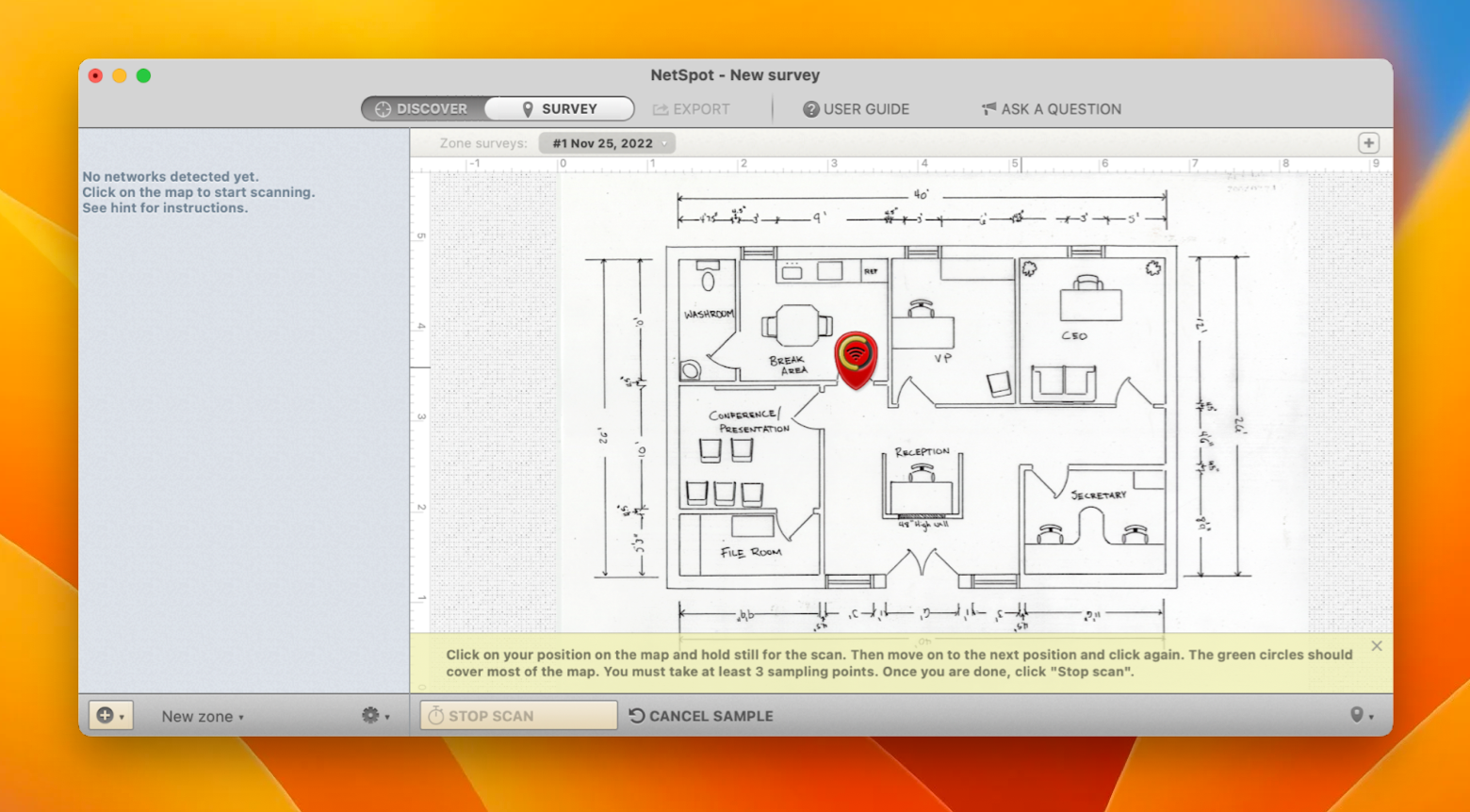
OS X: Taking better screenshots on a Mac.OS X Mavericks: 7 tips for the travelling Mac.An essential OS X Mavericks problem-solving guide.How do I get more out of Spotlight on Mavericks Macs.OS X: Everything you need to use Smart Folders.I hope this short report helps demystify and explain a little of what you can do with Wi-Fi Diagnostics. Security: The kind of encryption used - try to use WPA 2.BSSID: This is the identifier for your airport hardware.Other terms that may be useful when using this tool: You may eventually find a place in your space in which performance is better than anywhere else, or achieve better performance by switching off other computers or electrical devices. Given that some electrical devices (including devices situated in neighboring rooms and homes) and other networks can impact your performance, you might want to keep an eye on this while moving your Mac around. The Performance pane shows you the quality of your Wi-Fi over time. An SNR of 25 or above means you should have good performance. This is called the SNR (Signal to Noise Ratio) and the higher this number is the better your Wi-Fi performance will be. The difference between these numbers is the quality of your network, so if you have an RSSI of -47 and a Noise level of -96 then the difference is 49. Like RSSI this is measured in minus numbers, but a lower number is best, so a Noise level of -46 is better than one of -40. Neighboring networks, or the usual network interference culprits such as microwaves or some cordless phones, can impact your reception. Noise refers to the amount of wireless noise that may be affecting Wi-Fi reception. Higher numbers are better but because these are rated as minus numbers, it's important to note that an RSSI of -60 is actually much better than an RSSI of -80. The first refers to the strength of the signal between your Mac and your router. The Wi-Fi scan pane offers two metrics to help you determine this: Signal (RSSI, Received Signal Strength Indication) and Noise. You can use the information to determine the strength of your Wi-Fi signal (or use the Performance tab in this window to see how the tool sees your network performance in the Quality section to top left). If you find you are sharing a channel with others nearby, it helps to change the channel on your router to one the other networks aren't using - a clear channel usually improves reception quality. The first thing to check is what channel your network is on in comparison with other networks in your area. This shows you much information inside: Info, Logging and Performance windows A Frame Capture mode to sniff network traffic and a Wi-Fi Scan mode that captures useful info about your own and other networks in your area. While in Wireless Diagnostics, open the Utilities Window via the Menu bar ( Command-2). When you launch the app, a screen appears to tell you what the tool does and asks you to let it run tests to determine the state of your current Wi-Fi connection these can take a few minutes to complete. In the drop-down menu that appears, select "Open Wireless Diagnostics." The Wi-Fi Diagnostics app is hidden inside / System/Library/CoreServices/Applications, from where you can drag the app icon to make it easily available in your Dock. To access Wi-Fi Diagnostics, Option-click on the Wi-Fi icon in your Menu bar. Wi-Fi is essential to most Mac users, but what happens when your network gets sketchy? Apple's hidden Wi-Fi Diagnostics tool should help you improve Wi-Fi performance.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
